Heart Attack vs. Cardiac Arrest vs. Chest Pain: Spotting the Differences and When to Call 911
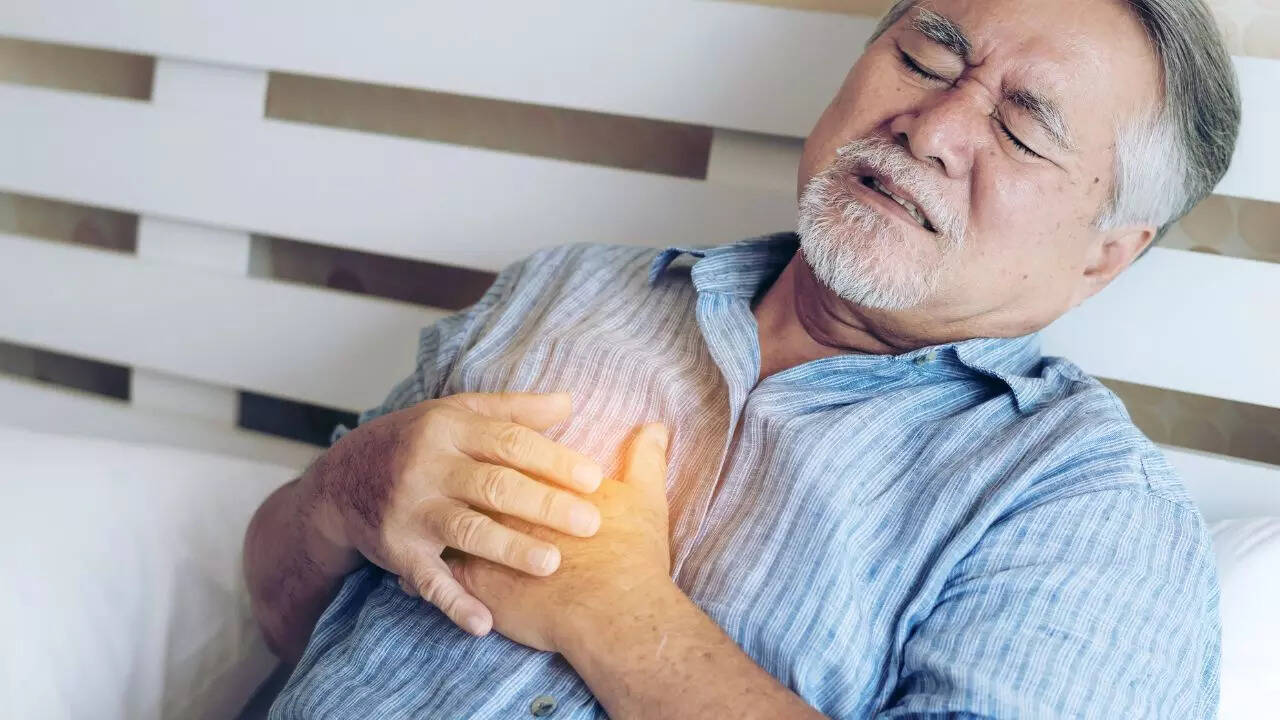
Experiencing chest pain? Knowing the difference between a heart attack, cardiac arrest, and simple chest pain is critical for your health and could be lifesaving. Understanding the symptoms and when to seek immediate medical help is key.
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is severely reduced or completely blocked. This blockage prevents the heart muscle from receiving the oxygen it needs. Cardiac arrest, on the other hand, is a sudden, unexpected loss of heart function. The heart abruptly stops beating effectively, halting blood flow to the brain and other vital organs.
Chest pain itself can stem from a variety of sources, ranging from indigestion to muscular strain. However, chest pain should never be ignored, especially if accompanied by other warning signs. It’s crucial to distinguish between harmless discomfort and a potentially life-threatening condition.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention: While the specific symptoms can vary, some common indicators warrant an immediate call to emergency services (911 or your local equivalent):
- Chest pain or discomfort: Pressure, tightness, squeezing, or pain in the chest, arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling breathless.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating or cold sweats.
- Nausea or vomiting: Feeling nauseous or vomiting.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: Feeling faint or dizzy.
- Sudden weakness: Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs.
- Sudden collapse: Collapsing or losing consciousness (common in cardiac arrest).
Preventive Measures: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle significantly reduces your risk of cardiovascular problems. Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking. Regular check-ups with your doctor are also essential for early detection and intervention.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.